- Understanding Vascular Inflammation and Heart Disease
- The Mechanisms Behind Vascular Inflammation
- How Vascular Inflammation Contributes to Atherosclerosis
- Real-World Examples of Inflammation and Heart Disease
- Strategies to Manage Vascular Inflammation for Heart Health
- Why HeartCare Hub Is Your Resource for Cardiovascular Wellness
1. Understanding Vascular Inflammation and Heart Disease
Heart disease is not solely the result of clogged arteries or high cholesterol; at its core, a significant driver is vascular inflammation. This biological process involves the immune system reacting within the blood vessels, often triggered by injury, infection, or chronic health conditions. While inflammation is part of the body’s natural defense, when persistent in blood vessels, it can damage the delicate lining of arteries, known as the endothelium, and set the stage for heart disease.
In everyday life, many individuals might overlook the subtle signs of vascular inflammation because they don’t cause obvious symptoms initially. However, the damage is quietly progressing, increasing the risk of serious cardiovascular events like heart attacks and strokes. Understanding vascular inflammation's role helps shift the focus toward prevention and early intervention.

2. The Mechanisms Behind Vascular Inflammation
Vascular inflammation begins when endothelial cells lining the arteries become dysfunctional due to factors such as high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, or elevated cholesterol levels. This dysfunction triggers an immune response where inflammatory cells—like macrophages and T-cells—accumulate in the arterial walls.
The release of inflammatory molecules, such as cytokines and chemokines, exacerbates tissue damage and attracts more immune cells, creating a vicious cycle. Over time, this process contributes to the formation of plaques, which narrow arteries and reduce blood flow.
Moreover, chronic inflammation can destabilize these plaques, making them prone to rupture, which often precipitates heart attacks. Research has shown that elevated inflammatory markers, including C-reactive protein (CRP), correlate strongly with increased cardiovascular risk.
Atlanta Heart Specialists
atlanta heart specialists
4375 Johns Creek Pkwy #350, Suwanee, GA 30024, USA

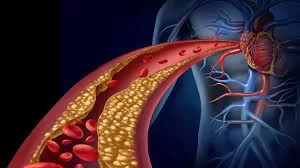
3. How Vascular Inflammation Contributes to Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis, the buildup of fatty deposits inside arteries, is a hallmark of heart disease. But it is the inflammatory response within the vessel walls that transforms these deposits into dangerous plaques. Inflammation attracts immune cells that ingest oxidized low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, turning into foam cells that accumulate and grow the plaques.
This ongoing inflammatory activity weakens the arterial wall and contributes to the development of fibrous caps. If the fibrous cap ruptures, it can lead to sudden clot formation and block the artery completely, causing a heart attack. Understanding this inflammatory cascade highlights why controlling vascular inflammation is critical in reducing heart disease risk.
4. Real-World Examples of Inflammation and Heart Disease
A compelling case involved a patient with persistent low-grade inflammation despite normal cholesterol levels. Advanced blood tests revealed elevated CRP levels, indicating vascular inflammation. After lifestyle changes and anti-inflammatory therapy, the patient’s inflammation markers decreased significantly, reducing their heart attack risk.
Another story involves emerging research linking autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis to higher rates of heart disease, mainly due to chronic systemic inflammation affecting blood vessels. These real-life insights illustrate how inflammation is a hidden but potent threat to heart health.
5. Strategies to Manage Vascular Inflammation for Heart Health
Effectively managing vascular inflammation requires a multi-pronged approach. Lifestyle modifications such as adopting an anti-inflammatory diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and omega-3 fatty acids can significantly reduce inflammation. Regular physical activity and quitting smoking also play vital roles.
Medications including statins, which lower cholesterol, have been shown to reduce inflammation independently. In certain cases, doctors might prescribe specific anti-inflammatory agents to target vascular inflammation directly.
Regular monitoring of inflammatory markers and cardiovascular risk factors can help guide treatment adjustments. Partnering with knowledgeable healthcare providers and utilizing resources like HeartCare Hub ensures patients receive tailored recommendations and support on this complex journey.
6. Why HeartCare Hub Is Your Resource for Cardiovascular Wellness
HeartCare Hub offers a comprehensive platform for anyone concerned about heart disease and vascular inflammation. Through expert advice, carefully curated health products, and access to specialized services, it empowers individuals to take control of their cardiovascular health.
Whether you are seeking guidance on lifestyle changes, inflammation testing, or advanced treatment options, HeartCare Hub provides up-to-date information and connects you to trusted professionals. This personalized support system makes it easier to navigate the complexities of heart disease prevention and management.
By leveraging resources available at HeartCare Hub, you can stay informed, reduce your vascular inflammation, and ultimately lower your risk of heart disease, safeguarding your heart’s health for years to come.





















Deborah Heart and Lung Center
deborah heart and lung center
200 Trenton Rd, Browns Mills, NJ 08015, USA