- Understanding Heart Disease: Causes and Impact
- Heart Transplant Overview: When and Why It’s Needed
- Steps in Heart Transplant Recovery and Rehabilitation
- Real-Life Case Study: A Journey Through Heart Transplant Recovery
- Long-Term Care and Support After a Heart Transplant
Understanding Heart Disease: Causes and Impact
Heart disease remains one of the leading causes of mortality worldwide, affecting millions of people every year. It encompasses a range of conditions, including coronary artery disease, heart failure, arrhythmias, and valve problems. The root causes often involve lifestyle factors such as poor diet, sedentary behavior, smoking, and genetic predisposition. High blood pressure and diabetes further increase the risk of developing serious cardiac issues.
Understanding heart disease is crucial because it often progresses silently until severe symptoms or life-threatening events occur. This silent progression underscores the importance of regular screenings and early interventions. When left untreated, heart disease can lead to irreversible damage, necessitating advanced treatments like heart transplants for some patients.

How Heart Disease Leads to Heart Transplant
In advanced cases, especially when heart failure becomes severe and unresponsive to medication, a heart transplant may be the only viable solution. Heart failure weakens the heart’s ability to pump blood efficiently, resulting in fatigue, fluid retention, and reduced quality of life. Patients eligible for heart transplants often have exhausted other treatment options, making this a critical, life-saving procedure.
Cardiac Solutions
cardiac solutions
5651 W Talavi Blvd, Glendale, AZ 85306, USA

Heart Transplant Overview: When and Why It’s Needed
A heart transplant involves replacing a diseased heart with a healthy donor heart, restoring cardiac function and dramatically improving survival rates for selected patients. The process requires careful evaluation by a multidisciplinary team to ensure the patient is an ideal candidate.
Eligibility for heart transplantation is determined by factors including age, overall health, severity of heart failure, and absence of other serious illnesses. The transplant list is highly competitive, and patients often endure long waiting periods. Advances in surgical techniques and immunosuppressive medications have significantly increased the success rates of heart transplants over the past decades.
Pre-Transplant Preparation
Before the transplant, patients undergo extensive testing and counseling to prepare for the physical and psychological challenges ahead. This preparation includes optimizing medical conditions, nutritional support, and education on post-transplant lifestyle changes.
Steps in Heart Transplant Recovery and Rehabilitation
Recovery from a heart transplant is a complex, multi-phase process that requires dedicated medical support and patient commitment. The initial hospital stay post-surgery typically lasts several weeks to monitor for complications such as rejection or infection.
Early Recovery Phase
During this phase, patients receive immunosuppressive drugs to prevent their immune system from attacking the new heart. Strict monitoring of heart function through biopsies and imaging is essential. Patients also start gentle physical rehabilitation to regain strength gradually.
Ongoing Rehabilitation
Cardiac rehabilitation plays a vital role in helping patients return to everyday life. This program includes supervised exercise, nutritional guidance, and psychological support to manage the emotional stress of transplant recovery. Maintaining medication adherence and regular follow-ups are critical to long-term success.
Real-Life Case Study: A Journey Through Heart Transplant Recovery
Consider the story of Mark, a 52-year-old who battled dilated cardiomyopathy for years before qualifying for a heart transplant. Post-surgery, Mark faced challenges such as medication side effects and the psychological impact of adjusting to a new heart. However, through diligent rehabilitation and support from his care team and family, he gradually regained strength and resumed an active lifestyle.
Mark’s experience highlights how recovery extends beyond physical healing. Emotional resilience and a strong support network are indispensable components of successful heart transplant recovery.
Long-Term Care and Support After a Heart Transplant
Living with a transplanted heart demands lifelong care. Patients must adhere to immunosuppressive therapy to prevent rejection and attend frequent medical check-ups. Additionally, managing risk factors like hypertension, diabetes, and infections is crucial.
Lifestyle Adjustments and Monitoring
Healthy lifestyle choices, including balanced nutrition, regular exercise, and stress management, contribute significantly to long-term health. It’s also important for patients to stay informed about potential complications and maintain open communication with their healthcare providers.
Resources for Patients
For those navigating the complexities of heart transplant recovery and heart disease management, resources like HeartCare Hub provide tailored recommendations for medications, support groups, and rehabilitation services. These resources empower patients to make informed decisions and access the best care available.
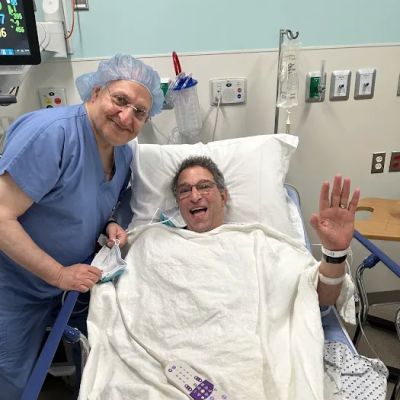





















Deborah Heart and Lung Center
deborah heart and lung center
200 Trenton Rd, Browns Mills, NJ 08015, USA