- Understanding Heart Disease and Physical Activity
- Why Exercise Is Crucial for Heart Disease Patients
- Key Exercise Benefits for Cardiac Health
- Practical Exercise Guidelines for People with Heart Disease
- Real-Life Stories Showcasing Exercise Success
- How HeartCare Hub Can Help with Exercise and Cardiac Support
1. Understanding Heart Disease and Physical Activity
Heart disease covers a wide range of conditions affecting the heart and blood vessels, such as coronary artery disease, heart attacks, and heart failure. These conditions often result in impaired blood flow and decreased heart function. Physical activity, once feared by some patients with heart disease, is now widely recognized as a powerful tool to enhance recovery and long-term heart health. Understanding the interaction between heart disease and exercise is key to managing the condition effectively.
Engaging in the right types and amounts of physical activity helps improve cardiovascular function, reduce symptoms, and promote overall wellbeing. However, exercise must be approached thoughtfully, tailored to individual health status, and ideally guided by healthcare professionals.

The evolving perspective on exercise
Historically, many heart disease patients were advised to limit physical exertion. Today, research confirms that controlled, regular exercise is beneficial and often essential in cardiac rehabilitation.
Cardiac Solutions
cardiac solutions
5651 W Talavi Blvd, Glendale, AZ 85306, USA

2. Why Exercise Is Crucial for Heart Disease Patients
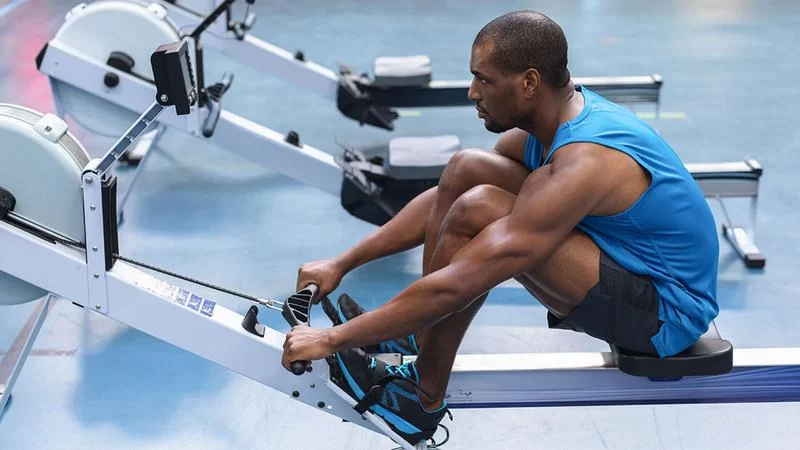
Exercise provides numerous benefits that directly impact heart disease outcomes and quality of life. By improving cardiovascular efficiency and strengthening the heart muscle, physical activity helps patients regain stamina and reduce the risk of further cardiac events.
Improving circulation and oxygen delivery
Regular exercise enhances the heart’s ability to pump blood efficiently, improving oxygen delivery to tissues. This helps counteract fatigue and shortness of breath often experienced by heart disease patients.
Reducing risk factors
Exercise helps lower blood pressure, improve cholesterol levels, and assist with weight management—all critical factors in controlling heart disease progression.
Mental health and motivation
Physical activity also improves mood and reduces anxiety and depression, which are common among heart disease patients, contributing to better adherence to treatment plans.
3. Key Exercise Benefits for Cardiac Health
The benefits of exercise in heart disease go beyond general fitness. Specific improvements are measurable and impactful.
Enhanced heart muscle strength and endurance
Regular aerobic exercise such as walking, cycling, or swimming strengthens the myocardium, making the heart more efficient and resilient.
Improved blood lipid profile
Exercise helps increase HDL (good cholesterol) and reduce LDL (bad cholesterol), slowing plaque buildup in arteries.
Better blood sugar control
Physical activity supports glucose metabolism, reducing the risk or severity of diabetes, which often coexists with heart disease.
Lower inflammation levels
Chronic inflammation is linked to heart disease progression; exercise helps reduce inflammatory markers.
4. Practical Exercise Guidelines for People with Heart Disease
Beginning or maintaining an exercise routine with heart disease requires caution and planning to ensure safety and maximize benefits.
Consult healthcare providers
Before starting any exercise program, patients should consult their cardiologist or rehabilitation specialist. This helps customize the intensity, type, and duration of physical activity based on individual needs.
Start slowly and build gradually
Light activities such as short walks or gentle stretching are good starting points. Over time, duration and intensity can increase as tolerated.
Include aerobic, strength, and flexibility exercises
Aerobic exercises improve endurance, strength training supports muscle health, and flexibility work reduces stiffness and injury risk.
Monitor symptoms carefully
Pay attention to signs like chest pain, excessive breathlessness, or dizziness. If any concerning symptoms occur, stop exercising and seek medical advice promptly.
5. Real-Life Stories Showcasing Exercise Success
Take Lisa’s story, a 65-year-old woman who survived a heart attack and initially felt too weak to be active. Encouraged by her cardiac rehab team, she began with daily 10-minute walks and gradually progressed to swimming sessions three times a week. Over the next year, Lisa reported increased energy, better sleep, and no further cardiac complications. Her experience highlights how consistent exercise transforms heart disease recovery.
Stories like Lisa’s are reminders that exercise is not just a recommendation but a lifeline. Many patients share how physical activity rekindled their confidence and helped them reclaim control over their health.
6. How HeartCare Hub Can Help with Exercise and Cardiac Support
For those navigating heart disease recovery, HeartCare Hub offers valuable resources including expert-curated products, fitness equipment suited for cardiac patients, and access to specialized coaching and rehabilitation services. Whether looking for heart rate monitors, comfortable workout gear, or tailored exercise programs, HeartCare Hub provides trustworthy options to support every step of your fitness journey.
Choosing the right tools and guidance through HeartCare Hub can make exercising safer, more effective, and enjoyable—empowering you to build a stronger, healthier heart with confidence.





















Deborah Heart and Lung Center
deborah heart and lung center
200 Trenton Rd, Browns Mills, NJ 08015, USA