Living with Implantable Heart Devices: Pacemakers and Defibrillators Explained
For millions of people worldwide, pacemakers and defibrillators are essential tools that help manage heart conditions and improve the quality of life. Whether you’ve just received an implant or are supporting someone who has, understanding how these devices work, their benefits, and how to live with them is crucial. This guide provides in-depth insights into living with implantable heart devices, including pacemakers and defibrillators, along with expert advice on managing them for a healthier life.

1. What Are Pacemakers and Defibrillators?
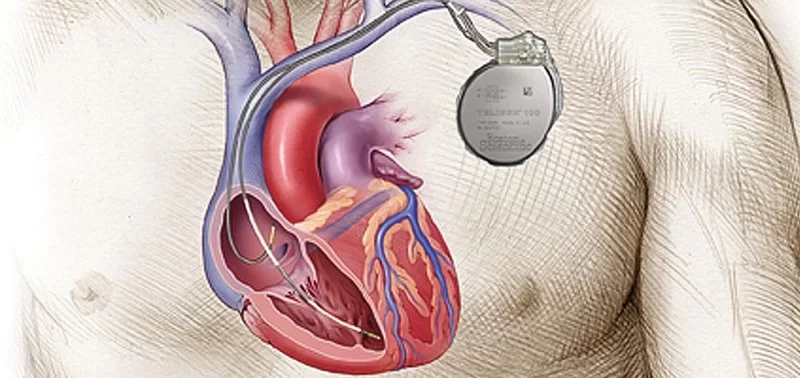
Pacemakers and defibrillators are small medical devices implanted in the chest to help regulate heart rhythm. Both devices serve similar purposes by addressing abnormal heartbeats (arrhythmias), but they do so in different ways:
- Pacemakers: These devices are used to regulate a slow or irregular heartbeat. They emit electrical impulses that prompt the heart to beat at a regular rhythm, ensuring that the heart pumps blood efficiently throughout the body.
- Defibrillators: Also known as implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs), defibrillators are used to treat dangerous arrhythmias, such as ventricular fibrillation. They deliver an electric shock to the heart when it detects life-threatening rhythms, effectively restoring normal heart activity.
2. How Do Pacemakers and Defibrillators Work?
Both pacemakers and defibrillators work through the same basic concept of electrical impulses, but their applications differ depending on the heart condition they are designed to treat. Here’s a closer look:
- Pacemakers: These devices are typically used for conditions like bradycardia, where the heart beats too slowly. The pacemaker monitors the heart's rhythm and, when necessary, sends small electrical pulses to help the heart maintain a steady, appropriate pace.
- Defibrillators: These devices are implanted in patients who experience more severe arrhythmias like ventricular fibrillation or ventricular tachycardia. The ICD monitors the heart and can deliver a shock if an abnormal rhythm that could lead to cardiac arrest is detected.
In both cases, the devices are equipped with advanced sensors to detect irregular heart rhythms and respond accordingly, ensuring that the heart keeps beating in a life-sustaining manner.
Atlanta Heart Specialists
atlanta heart specialists
4375 Johns Creek Pkwy #350, Suwanee, GA 30024, USA

3. The Benefits of Pacemakers and Defibrillators
Pacemakers and defibrillators provide significant benefits, especially for individuals suffering from arrhythmias or other heart conditions. These benefits can improve both the quality and longevity of life:
- Improved Heart Function: By ensuring that the heart maintains a steady rhythm, these devices help improve blood flow, allowing for better oxygen and nutrient delivery to the body.
- Prevention of Sudden Cardiac Arrest: For patients at risk of sudden cardiac arrest, the defibrillator can be lifesaving, providing immediate intervention that can restore normal heart rhythms.
- Enhanced Confidence and Mobility: Individuals with pacemakers and defibrillators often report feeling more confident in their ability to engage in daily activities. The peace of mind knowing that the device will intervene in case of an emergency allows for greater freedom.
- Reduced Symptoms: For patients with bradycardia or irregular heart rhythms, these devices reduce symptoms such as dizziness, fatigue, and shortness of breath, leading to improved overall well-being.
4. Living with Pacemakers and Defibrillators: What to Expect
While pacemakers and defibrillators can greatly improve health outcomes, living with an implantable heart device requires some lifestyle adjustments and regular care. Here are key considerations for those living with these devices:
4.1. Regular Check-ups
Patients with pacemakers and defibrillators need to have regular follow-up appointments with their healthcare provider. These appointments are essential for checking the device’s battery life, functionality, and making any necessary adjustments. Over time, pacemakers and defibrillators may require updates or reprogramming to ensure they’re providing optimal care.
4.2. Activity Restrictions
After the implantation of a pacemaker or defibrillator, there are typically some activity restrictions, especially during the initial recovery phase. Patients may be advised to avoid heavy lifting, intense exercise, or any activities that could strain the chest area. However, most patients can gradually return to normal physical activity after the device has fully settled.
4.3. Avoiding Electromagnetic Interference
Since pacemakers and defibrillators are powered by electricity, it's essential to be aware of potential sources of electromagnetic interference (EMI), which could disrupt the device’s function. Devices such as powerful magnets, some MRI machines, or high-voltage equipment can interfere with the normal operation of the heart devices. Patients should be aware of these and inform their healthcare providers about any potential risks during check-ups or procedures.
4.4. Adjusting Lifestyle Habits
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is crucial for anyone with a pacemaker or defibrillator. This includes eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly (as advised by your doctor), avoiding smoking, and managing stress levels. A healthy lifestyle will not only help support the function of your device but will also improve your overall heart health.
5. Real-life Experiences of Pacemaker and Defibrillator Patients
For many people with heart conditions, a pacemaker or defibrillator offers more than just medical assistance—it provides a sense of security and hope. Here’s a brief story from one patient, Anna, who had a pacemaker implanted:
“I was diagnosed with bradycardia, and I was always exhausted, feeling light-headed and unable to keep up with my usual activities. My doctor suggested a pacemaker, and although I was initially nervous, the procedure was quick and recovery was surprisingly easy. Now, I can go for walks, work, and even play with my kids without worrying about feeling dizzy. The pacemaker has truly changed my life for the better.”
Similarly, for John, who had a defibrillator implanted after a life-threatening arrhythmia:
“Having the defibrillator has given me peace of mind. I’m not afraid of sudden cardiac arrest anymore, and I can enjoy my life without worrying about my heart condition. Knowing that the defibrillator is there to intervene if needed is a huge relief.”
6. How to Care for Your Pacemaker or Defibrillator
Caring for your pacemaker or defibrillator involves simple yet crucial steps. Regular device check-ups, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and staying informed about potential risks can help ensure that your heart device remains in optimal condition.
Final Thoughts: Embracing a Heart-Healthy Life with Implantable Devices
Living with pacemakers and defibrillators doesn’t have to be a challenge. With proper care, lifestyle modifications, and regular medical supervision, these devices can allow you to live an active and fulfilling life. The key is to stay informed, follow your healthcare provider’s advice, and embrace the changes that come with having a device that’s working for your heart health.




















Deborah Heart and Lung Center
deborah heart and lung center
200 Trenton Rd, Browns Mills, NJ 08015, USA