- 1-Understanding-the-Connection-Between-Heart-Disease-and-Depression
- 2-How-Depression-Affects-Heart-Health
- 3-Physiological-and-Behavioral-Factors-Linking-the-Two-Conditions
- 4-Real-Life-Stories-of-the-Heart-Disease-Depression-Link
- 5-Strategies-for-Managing-Both-Conditions-Effectively
1. Understanding the Connection Between Heart Disease and Depression
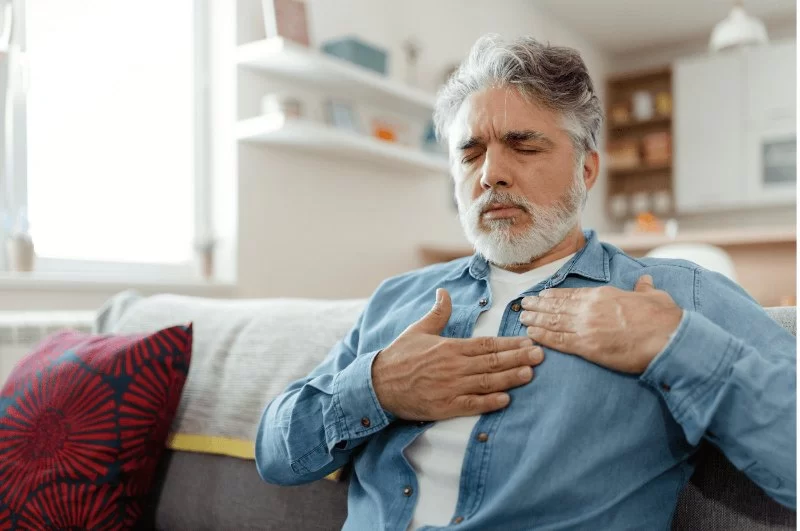
The link between heart disease and depression is well-established in medical research, highlighting a complex relationship where each condition can influence the other. Depression not only affects emotional wellbeing but also has tangible effects on cardiovascular health, increasing the risk of heart disease and complicating its treatment.
People diagnosed with heart disease are more prone to developing depression, and those with depression are at a higher risk for cardiovascular problems. This bidirectional relationship underscores the need for integrated care approaches.

1.1 Prevalence of Depression in Heart Disease Patients
Studies show that nearly one in five patients with heart disease experiences major depression, significantly impacting recovery and quality of life.
Atlanta Heart Specialists
atlanta heart specialists
4375 Johns Creek Pkwy #350, Suwanee, GA 30024, USA

1.2 Impact on Mortality and Morbidity
Depression in heart disease patients is linked to increased mortality, highlighting the seriousness of this connection beyond emotional distress.
2. How Depression Affects Heart Health
Depression influences heart health through both physiological and behavioral pathways. Physiologically, it triggers chronic inflammation, increases cortisol levels, and disrupts autonomic nervous system balance, all of which strain the cardiovascular system.
Behaviorally, depression often leads to poor lifestyle choices such as smoking, sedentary habits, and neglecting medication, further exacerbating heart disease risk.
2.1 Inflammation and Stress Hormones
Elevated inflammation and cortisol contribute to plaque buildup and arterial damage, raising the chance of heart attacks and strokes.
2.2 Lifestyle Challenges
Depressed individuals may find it difficult to maintain healthy routines, adhere to treatments, or seek timely medical help.
3. Physiological and Behavioral Factors Linking the Two Conditions
The heart disease and depression link is reinforced by overlapping risk factors and biological mechanisms:
3.1 Shared Risk Factors
Obesity, diabetes, and high blood pressure increase the likelihood of both depression and heart disease.
3.2 Neurochemical Imbalances
Changes in neurotransmitters such as serotonin affect mood and cardiovascular function simultaneously.
3.3 Medication Interactions
Some heart medications may influence mood, and certain antidepressants have cardiovascular side effects, necessitating careful management.
4. Real-Life Stories of the Heart Disease and Depression Link
John, a 58-year-old heart attack survivor, experienced severe depression during recovery, which hindered his rehabilitation progress. With comprehensive care involving cardiologists and mental health professionals from HeartCare Hub, John managed to regain both physical and emotional strength.
Such cases highlight how addressing both heart disease and depression together improves outcomes and quality of life.
4.1 Emotional Toll and Recovery
Patients often describe depression as a hidden burden that complicates their physical healing journey.
4.2 Importance of Support Networks
Family, healthcare teams, and peer support play vital roles in managing this dual challenge.
5. Strategies for Managing Both Conditions Effectively
Integrated treatment plans focusing on physical and mental health are essential. Strategies include:
5.1 Collaborative Healthcare Approach
Cardiologists working alongside psychologists and psychiatrists ensure comprehensive care addressing all aspects of health.
5.2 Lifestyle Modifications
Regular exercise, healthy diet, stress reduction techniques, and quitting smoking benefit both heart and mental health.
5.3 Medication and Therapy
Appropriate use of antidepressants and counseling complements cardiac treatments.
For personalized advice and resources on the heart disease and depression link, visit HeartCare Hub, where expert guidance helps you navigate these interconnected health challenges with confidence.





















Deborah Heart and Lung Center
deborah heart and lung center
200 Trenton Rd, Browns Mills, NJ 08015, USA