- 1 - What Are Calcium Channel Blockers?
- 2 - How Calcium Channel Blockers Support Heart Health
- 3 - Types and Common Examples
- 4 - Patient Stories and Real Experiences
- 5 - Possible Side Effects and Precautions
- 6 - Combining Medication with Lifestyle for Better Results
1. What Are Calcium Channel Blockers?
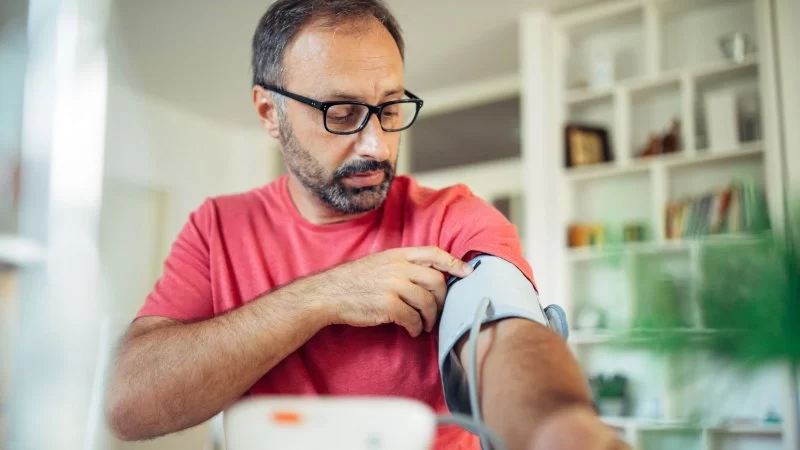
Calcium channel blockers, also known as CCBs, are a group of medications that relax blood vessels by preventing calcium from entering the cells of the heart and arteries. Since calcium plays a key role in muscle contraction, blocking its flow helps blood vessels widen, allowing smoother blood circulation. These medications are widely used to manage high blood pressure, chest pain (angina), and certain heart rhythm disorders.

2. How Calcium Channel Blockers Support Heart Health
By reducing the force of contraction in the heart and widening arteries, calcium channel blockers help decrease the workload on the heart. For individuals struggling with hypertension, this can be life-changing. Lowering blood pressure not only reduces the risk of heart attack and stroke but also protects organs like the kidneys and brain from long-term damage. Many cardiologists in the U.S. recommend CCBs as part of a treatment plan tailored to patient needs, especially when other blood pressure medications are insufficient.
Capital Health Medical Center – Hopewell
capital health medical center hopewell
1 Capital Way, Pennington, NJ 08534, USA

Benefits Beyond Blood Pressure
Calcium channel blockers also improve oxygen delivery to the heart muscle, making them effective for people with chronic angina. Some types can slow heart rate, which is helpful for certain arrhythmias. This versatility makes them a cornerstone in modern cardiovascular medicine.
3. Types and Common Examples
There are two main types of calcium channel blockers: dihydropyridines and non-dihydropyridines. Each has slightly different effects and is prescribed based on patient condition.
Dihydropyridines
These primarily affect blood vessels, making them effective for lowering blood pressure. Common examples include amlodipine and nifedipine. Patients often find these medications easier to tolerate for long-term use.
Non-Dihydropyridines
These influence both the heart and blood vessels, slowing heart rate while relaxing arteries. Examples include verapamil and diltiazem. They are often prescribed for arrhythmias or angina.
4. Patient Stories and Real Experiences
Consider the story of a 58-year-old teacher in California who had struggled with uncontrolled high blood pressure despite trying multiple medications. When her doctor introduced amlodipine, she noticed her blood pressure stabilized within weeks, and she experienced fewer headaches and less fatigue. Another case involved a New York firefighter who suffered frequent angina episodes. After starting diltiazem, he regained confidence in physical activity and reported feeling “like he had his life back.” Stories like these highlight the real-world effectiveness of calcium channel blockers for managing heart conditions.
5. Possible Side Effects and Precautions
Like any medication, calcium channel blockers come with possible side effects. The most common include dizziness, swollen ankles, constipation, and headaches. In rare cases, they may cause more serious effects like low heart rate or severe swelling. Patients should always follow up with their healthcare providers if symptoms persist or worsen. It’s important to avoid abruptly stopping the medication, as this could trigger chest pain or elevated blood pressure.
Who Should Be Careful
Patients with certain conditions, such as heart failure or liver disease, may require special monitoring before starting these drugs. This is why consulting a trusted healthcare provider or specialized service such as HeartCare Hub is critical for safe use.
6. Combining Medication with Lifestyle for Better Results
While calcium channel blockers are effective on their own, their benefits multiply when paired with healthy lifestyle changes. Regular exercise, a balanced diet low in sodium, and stress management amplify their heart-protective effects. Patients who incorporate these habits often require lower doses and report fewer side effects.
A Holistic Approach
Heart health is not about relying on medication alone. It’s about adopting a comprehensive strategy that includes medical treatment, lifestyle improvements, and ongoing professional support. For many Americans, calcium channel blockers provide the foundation, while daily habits and expert care ensure lasting results.





















Deborah Heart and Lung Center
deborah heart and lung center
200 Trenton Rd, Browns Mills, NJ 08015, USA