1. Understanding Saturated Fats: What Are They Really?
Saturated fats have long been a controversial topic in the world of nutrition. Once vilified as a major contributor to heart disease and obesity, these fats have been the subject of intense debate in recent years. But what exactly are saturated fats, and why have they earned such a bad reputation?
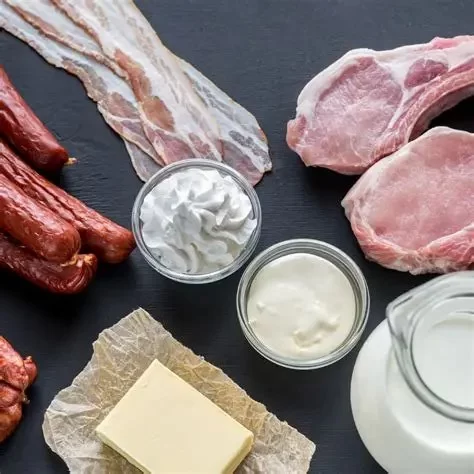
Saturated fats are fats that are solid at room temperature and are typically found in animal products such as butter, cheese, and fatty cuts of meat. They are also present in some plant-based oils like coconut oil and palm oil. Understanding the nature of saturated fats is essential before diving into the complexities of how they affect our health.
2. The Evolution of Dietary Guidelines Regarding Saturated Fats
The first dietary guidelines to reduce saturated fat intake came out in the 1970s, driven by concerns about heart disease. For decades, nutritionists and health experts recommended that people reduce their consumption of foods high in saturated fats, replacing them with unsaturated fats found in plant oils, nuts, and seeds. But recent research has called some of these guidelines into question.
2.1. Changing Science: The Shift in Perspective
In the past decade, several studies have suggested that the link between saturated fat and heart disease may not be as clear-cut as once thought. While high levels of saturated fat consumption may raise LDL cholesterol (often labeled as "bad" cholesterol), recent evidence shows that the correlation between saturated fats and heart disease is much weaker than previously believed. In fact, some studies have even indicated that certain sources of saturated fats, like those found in dairy, may have a neutral or even beneficial effect on heart health.
2.2. What Current Research Says About Saturated Fat Consumption
Today, many nutrition experts argue that focusing solely on saturated fat intake may be too simplistic. Instead, it is essential to consider the overall quality of one's diet. For example, replacing saturated fats with refined carbohydrates, rather than healthy fats, does not reduce the risk of heart disease and may even increase it. Furthermore, it's important to consider where the saturated fats are coming from—coconut oil and fatty fish, for instance, may not have the same health effects as processed meats.
3. Healthy Fats vs. Unhealthy Fats: A Deeper Dive
To truly understand the role of fats in our diet, it's important to distinguish between healthy and unhealthy fats. While saturated fats often get a bad reputation, they are not all created equal. The impact of fat on your health depends not just on the type of fat, but also on the source and context of its consumption.
3.1. Healthy Sources of Saturated Fats
Not all sources of saturated fats are detrimental to health. In fact, some sources can be part of a balanced, heart-healthy diet. For example, dark chocolate, grass-fed butter, and coconut oil contain moderate amounts of saturated fats that, when consumed in moderation, may offer certain health benefits, including antioxidant properties and anti-inflammatory effects. The key lies in moderation and sourcing these fats from nutrient-dense, whole food sources.
3.2. Unhealthy Sources of Saturated Fats
On the other hand, processed and fast foods that are high in saturated fats, such as fried foods, packaged snacks, and processed meats, are best avoided or limited. These foods often contain unhealthy trans fats and refined sugars, which pose a greater risk to heart health. By opting for whole, minimally processed foods, you can reduce your intake of these harmful fats and improve overall health.
4. The Impact of Saturated Fats on Heart Health: What We Know Now
While the relationship between saturated fats and heart disease remains a subject of debate, it’s crucial to focus on overall dietary patterns rather than obsessing over individual nutrients. Some studies suggest that moderate intake of saturated fats does not significantly increase heart disease risk, especially when consumed as part of a diet rich in whole foods like vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and healthy fats.
4.1. Focusing on a Healthy Lifestyle
What is becoming clearer from the latest research is that heart health is influenced by a variety of factors, including physical activity, stress management, and weight maintenance. It’s important to focus on a holistic, heart-healthy lifestyle, which includes not just eating the right fats but also managing other aspects like blood pressure, sleep, and exercise. A balanced diet, rather than one fixated on cutting out certain fats, is essential for long-term heart health.
4.2. HeartCare Hub: Your Guide to Heart-Healthy Fats
At HeartCare Hub, we aim to provide you with the most current, science-backed information to help you make informed decisions about your diet and lifestyle. If you're looking to incorporate heart-healthy fats into your meals, explore our selection of products that focus on healthy fat sources like olive oil, avocados, nuts, and seeds. Our expert recommendations can guide you toward maintaining a balanced diet that supports overall heart health.