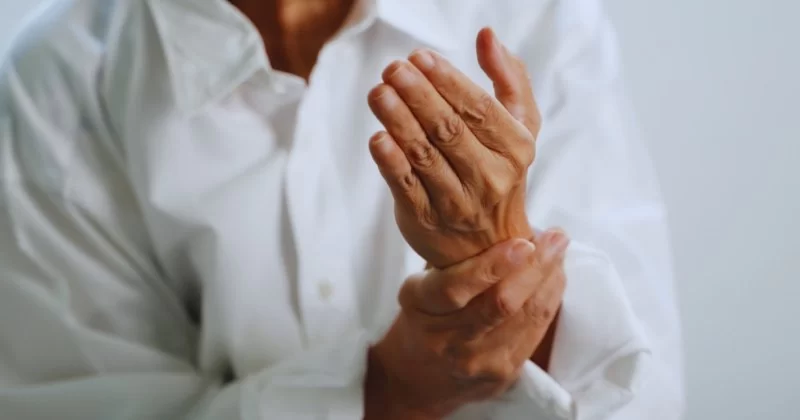
- what-is-rheumatoid-arthritis-systemic-and-beyond-joints - What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis? Systemic and Beyond Joints
- how-systemic-inflammation-in-ra-affects-heart-health - How Systemic Inflammation in RA Affects Heart Health
- case-study-living-with-ra-and-facing-heart-complications - Case Study: Living with RA and Facing Heart Complications
- the-importance-of-early-diagnosis-and-integrated-care - The Importance of Early Diagnosis and Integrated Care
- how-to-protect-your-heart-if-you-have-rheumatoid-arthritis - How to Protect Your Heart if You Have Rheumatoid Arthritis
- resources-and-support-for-patients-at-heartcare-hub - Resources and Support for Patients at HeartCare Hub
1. What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis? Systemic and Beyond Joints
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is commonly understood as a chronic autoimmune condition that targets the joints. However, in reality, RA is far more than joint pain and stiffness—it’s a systemic inflammatory disease. This means the immune system doesn’t just attack cartilage and bone, but can also affect blood vessels, the heart, lungs, and other organs.
In the United States alone, nearly 1.3 million people live with RA, and many are unaware that their condition can place them at significantly higher risk for cardiovascular disease. Understanding this connection is essential—not only for effective RA treatment, but also for long-term heart health.

2. How Systemic Inflammation in RA Affects Heart Health
2.1 Inflammation Is a Shared Enemy
The chronic inflammation that defines rheumatoid arthritis doesn’t just stay in the joints—it travels through the bloodstream, impacting vascular health. Cytokines like tumor necrosis factor (TNF-alpha) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) are elevated in RA and contribute to arterial plaque buildup and endothelial dysfunction. The result? A significantly increased risk of heart attack, stroke, and other forms of cardiovascular disease.
Atlanta Heart Specialists
atlanta heart specialists
4375 Johns Creek Pkwy #350, Suwanee, GA 30024, USA

2.2 Cardiovascular Disease Is the Leading Cause of Death in RA Patients
Studies show that people with RA are nearly twice as likely to develop heart disease compared to the general population. This is particularly concerning given that traditional risk factors (like cholesterol and hypertension) don’t always explain the elevated risk. Inflammatory pathways appear to be the primary drivers.
3. Case Study: Living with RA and Facing Heart Complications
Meet Sandra, a 52-year-old school counselor from Austin, Texas. Diagnosed with RA at age 44, she initially focused her efforts on reducing joint pain through medication and physical therapy. It wasn’t until she experienced an episode of chest pain and was later diagnosed with a minor heart attack that she learned RA was also targeting her cardiovascular system.
“It was a wake-up call,” she recalls. “I had no idea my joints and my heart were in the same battle.” Since then, Sandra has adopted a more holistic approach, working with a rheumatologist and a cardiologist who communicate regularly. Her story is one of many highlighting the need for integrated care.
4. The Importance of Early Diagnosis and Integrated Care
4.1 Screening Beyond the Joints
Clinicians now emphasize the need for regular cardiovascular screenings in RA patients—even in those who don't present traditional cardiac symptoms. Tests such as echocardiograms, carotid ultrasounds, and inflammation markers (like CRP and ESR) can reveal early warning signs before heart disease becomes symptomatic.
4.2 Coordination Between Specialties
Integrated care models are proving to be highly effective. Rheumatologists and cardiologists working together are more likely to develop treatment plans that minimize both joint damage and heart complications. Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) like methotrexate and biologics such as TNF inhibitors may even reduce cardiovascular risk when prescribed early.
5. How to Protect Your Heart if You Have Rheumatoid Arthritis
5.1 Lifestyle Adjustments That Matter
Adopting heart-healthy habits is essential for people with RA. This includes regular low-impact exercise like swimming or yoga, a Mediterranean-style anti-inflammatory diet, stress management practices, and strict smoking cessation. These small adjustments can have outsized effects on both joint and heart health.
5.2 Medication Matters Too
Always discuss with your healthcare provider whether your RA treatment is also supporting your cardiovascular health. Some medications, such as corticosteroids, may worsen heart risk when used long-term, while others like statins can play a protective role when prescribed appropriately.
6. Resources and Support for Patients at HeartCare Hub
If you or a loved one is living with RA, it’s important to stay informed, proactive, and supported. At HeartCare Hub, we offer a wealth of information, tools, and personalized care recommendations for those navigating the complexities of RA and heart health. Whether you're looking for the latest research, access to compassionate specialists, or practical lifestyle guidance, we’re here to support your journey.
Because caring for your joints should never come at the cost of your heart—and with the right guidance, you don’t have to choose.





















Deborah Heart and Lung Center
deborah heart and lung center
200 Trenton Rd, Browns Mills, NJ 08015, USA