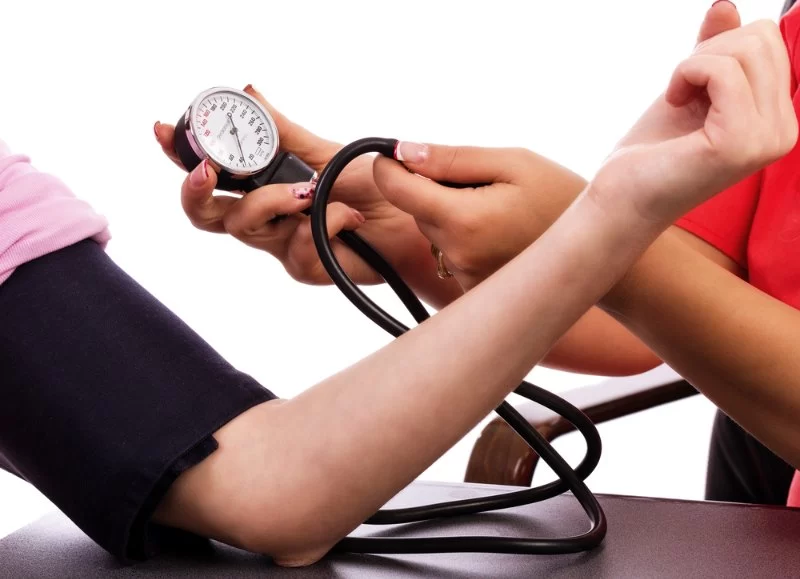
- 1 - The Role of Magnesium in Blood Pressure Regulation
- 2 - Scientific Evidence on Magnesium Supplements
- 3 - Choosing the Right Magnesium Supplement
- 4 - Recommended Dosage and Safety Considerations
- 5 - Real-Life Experiences with Magnesium for Blood Pressure
- 6 - Integrating Magnesium into a Heart-Healthy Lifestyle
1. The Role of Magnesium in Blood Pressure Regulation
Magnesium is an essential mineral that plays a vital role in maintaining normal blood pressure levels. It helps relax blood vessels, supports proper muscle function, and balances electrolytes—factors directly influencing cardiovascular health. For individuals dealing with hypertension, magnesium’s vasodilating effect can reduce strain on the heart and improve circulation. Studies have shown that low magnesium levels are often linked to higher blood pressure, making supplementation a potential support strategy for those at risk.

2. Scientific Evidence on Magnesium Supplements
Multiple peer-reviewed studies have confirmed that magnesium supplementation can help lower blood pressure, particularly in people with mild to moderate hypertension. A 2017 meta-analysis found that daily magnesium intake was associated with a small but significant reduction in both systolic and diastolic pressure. The mechanism lies in magnesium’s ability to regulate calcium and potassium flow in cells, which impacts blood vessel constriction. Although it’s not a standalone cure, magnesium works well alongside other heart-healthy interventions.
3. Choosing the Right Magnesium Supplement
Not all magnesium supplements are created equal. Forms like magnesium citrate and magnesium glycinate are more bioavailable, meaning your body can absorb them more efficiently. Magnesium oxide, while more affordable, may be less effective and more likely to cause digestive discomfort. When selecting a supplement, consider your dietary intake, digestive sensitivity, and whether you need additional benefits, such as improved sleep or muscle relaxation. Brands recommended by cardiovascular specialists often emphasize purity and clinically tested absorption rates.
4. Recommended Dosage and Safety Considerations
The recommended daily intake for magnesium varies by age and sex, but for most adults, it ranges between 310–420 mg. It’s important not to exceed the tolerable upper intake level of 350 mg from supplements unless directed by a healthcare professional. Excess magnesium can lead to gastrointestinal issues and, in rare cases, more serious side effects like irregular heartbeat. If you’re taking medications for blood pressure or heart disease, consult your doctor before adding magnesium to avoid potential interactions.
5. Real-Life Experiences with Magnesium for Blood Pressure
One patient shared how, after struggling with fluctuating blood pressure despite lifestyle changes, adding magnesium glycinate to their routine made a noticeable difference within weeks. They reported not only steadier readings but also better sleep and reduced muscle cramps. Another case involved a middle-aged runner who used magnesium to manage post-exercise blood pressure spikes, helping them maintain cardiovascular stability during training season. These experiences highlight how magnesium can complement broader health strategies when used responsibly.
6. Integrating Magnesium into a Heart-Healthy Lifestyle
While supplements can be helpful, magnesium-rich foods should also be a priority. Leafy greens, nuts, seeds, whole grains, and legumes are excellent natural sources. Combining a magnesium-rich diet with regular exercise, stress management, and limiting sodium intake creates a strong foundation for blood pressure control. For those seeking expert guidance and quality supplement recommendations, HeartCare Hub offers tailored resources to support cardiovascular wellness.





















Daniel M. Sauri, MD
blood pressure 136/56
800 Biesterfield Rd, Elk Grove Village, IL 60007, USA