- Connection Between High-Fat Diets and Heart Disease
- Types of Fats and Their Impact on Cardiovascular Health
- Real-World Examples and Scientific Studies
- Managing Your Diet for Better Heart Health
- How HeartCare Hub Supports Your Heart Health Journey
1. Connection Between High-Fat Diets and Heart Disease
Understanding the connection between high-fat diets and heart disease requires a deep dive into how different types of fats affect the cardiovascular system. Historically, diets high in fat—particularly saturated and trans fats—have been linked to increased risk of heart disease. This association largely stems from their influence on blood cholesterol levels and arterial health.
Heart disease, which includes conditions like coronary artery disease and heart attacks, often arises when arteries become narrowed or blocked due to fatty deposits, known as atherosclerosis. High-fat diets can accelerate this process by raising low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, often referred to as “bad cholesterol.” Elevated LDL levels contribute to plaque buildup inside artery walls, reducing blood flow and increasing the risk of cardiac events.
Yet, not all fats have the same effect. The link between fat intake and heart disease is nuanced, and the type of fat consumed plays a crucial role in either promoting or protecting heart health.

1.1 How Fat Influences Heart Disease Risk
When consuming a diet rich in saturated fats—found in red meat, butter, and certain dairy products—LDL cholesterol tends to increase, which can accelerate the development of heart disease. On the other hand, unsaturated fats, particularly omega-3 fatty acids found in fish, nuts, and seeds, have protective effects by lowering inflammation and improving cholesterol profiles.
Scientific evidence points toward replacing saturated fats with unsaturated fats as a key strategy to reduce cardiovascular risk. This highlights the importance of not only the quantity of fat in the diet but its quality and source.
Capital Health Medical Center – Hopewell
capital health medical center hopewell
1 Capital Way, Pennington, NJ 08534, USA

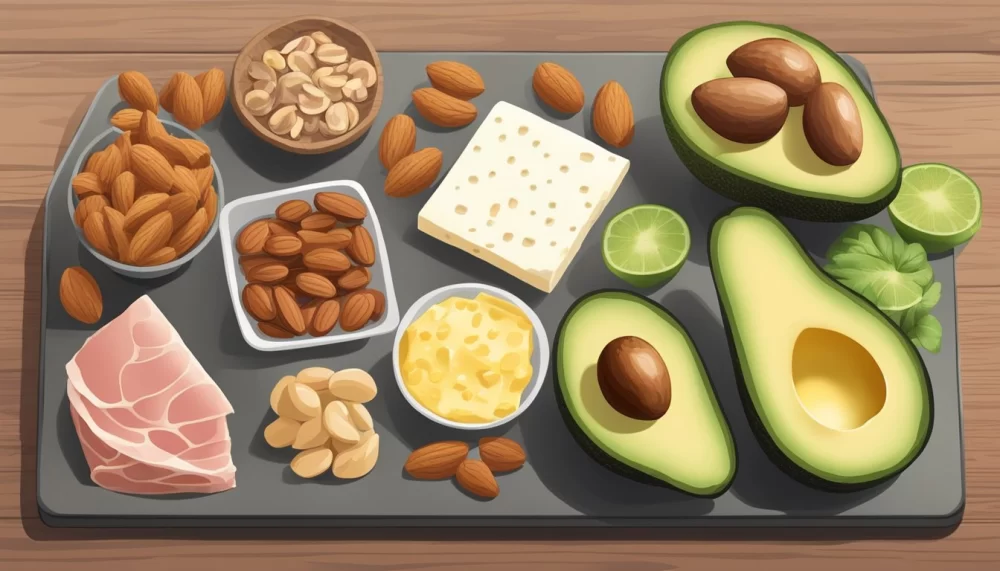
2. Types of Fats and Their Impact on Cardiovascular Health
Dietary fats can be broadly categorized into saturated fats, unsaturated fats (monounsaturated and polyunsaturated), and trans fats. Each affects heart health differently:
2.1 Saturated Fats
Saturated fats are typically solid at room temperature and are common in animal products like fatty cuts of meat, butter, cheese, and some tropical oils such as coconut and palm oil. Excessive consumption of saturated fats has been linked to raised LDL cholesterol and increased heart disease risk. However, recent studies suggest that the context of overall diet quality and individual metabolic health also influences this risk.
2.2 Unsaturated Fats
Unsaturated fats, found in olive oil, avocados, nuts, and fatty fish like salmon, are known to improve heart health. They help reduce LDL cholesterol while increasing high-density lipoprotein (HDL), the “good cholesterol.” Omega-3 fatty acids specifically provide anti-inflammatory benefits that protect the heart and blood vessels.
2.3 Trans Fats
Artificial trans fats, often present in processed foods and baked goods, are the most harmful fats for cardiovascular health. They raise LDL cholesterol and lower HDL cholesterol simultaneously, significantly increasing heart disease risk. Many countries have taken steps to ban or limit trans fats due to their well-documented dangers.
3. Real-World Examples and Scientific Studies
To bring this discussion to life, consider the famous "Seven Countries Study," which linked dietary fat consumption patterns to rates of heart disease across different populations. Mediterranean countries, with diets rich in unsaturated fats from olive oil and nuts, showed lower heart disease rates compared to countries consuming more saturated fats.
Another example is the story of John, a middle-aged man diagnosed with early signs of heart disease. His diet was heavy in processed meats and fried foods, rich in saturated and trans fats. After consulting with healthcare professionals and switching to a diet focusing on healthy fats, fruits, and vegetables, John’s cholesterol levels improved dramatically, and his heart health stabilized. This illustrates how dietary changes can have real, positive impacts.
Additionally, numerous controlled trials have demonstrated that reducing saturated fat intake while increasing unsaturated fat consumption leads to better cardiovascular outcomes, confirming the practical importance of understanding fat types.
4. Managing Your Diet for Better Heart Health
For anyone concerned about heart disease risk, managing fat intake thoughtfully is crucial. Here are several strategies that integrate scientific insights and practical advice:
4.1 Prioritize Healthy Fats
Focus on consuming more monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats through foods like olive oil, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish. These fats support healthy cholesterol levels and reduce inflammation.
4.2 Limit Saturated Fat Intake
Reduce consumption of high-fat dairy products, fatty meats, and tropical oils. Instead, choose lean proteins and plant-based fat sources where possible.
4.3 Avoid Trans Fats
Carefully check food labels to avoid artificial trans fats often hidden in processed and fried foods. Cooking at home with fresh ingredients can significantly help reduce this risk factor.
4.4 Adopt a Heart-Healthy Lifestyle
Beyond diet, regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding smoking are essential components of cardiovascular health. Combining these efforts amplifies the benefits of a heart-friendly diet.
5. How HeartCare Hub Supports Your Heart Health Journey
Understanding the complex relationship between diet and heart disease can be overwhelming. HeartCare Hub offers tailored resources, expert advice, and product recommendations to help you make informed decisions about your cardiovascular health. Whether you’re seeking heart-healthy foods, supplements, or lifestyle guidance, our platform connects you to trusted options designed to support your well-being.
Explore HeartCare Hub to find personalized recommendations that fit your unique health goals, helping you reduce heart disease risk through smarter dietary choices and proven strategies.





















Deborah Heart and Lung Center
deborah heart and lung center
200 Trenton Rd, Browns Mills, NJ 08015, USA