- 1 - The Role of Sodium in Your Body
- 2 - How Sodium Affects Blood Pressure
- 3 - Health Risks of Excessive Sodium Intake
- 4 - Tips for Reducing Sodium Intake
- 5 - How HeartCare Hub Can Help Manage Your Sodium Intake
1 - The Role of Sodium in Your Body
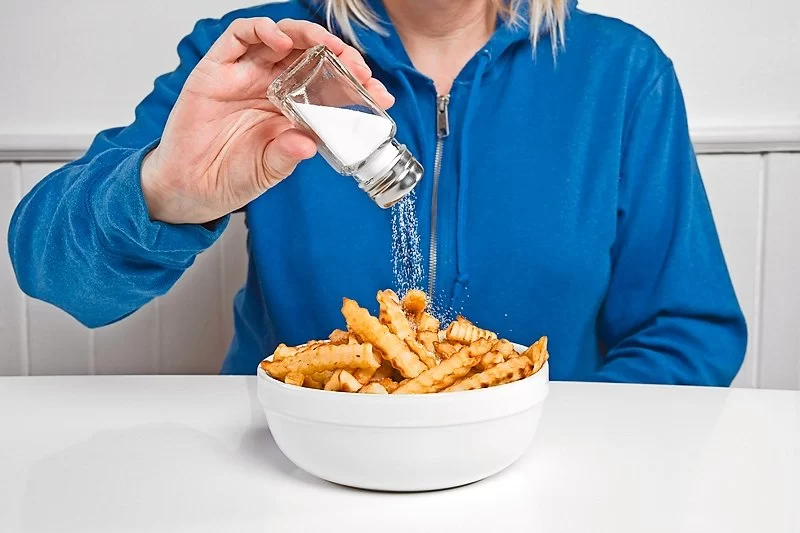
Sodium is an essential mineral that plays a vital role in various bodily functions, such as regulating fluid balance, muscle function, and nerve transmission. However, while sodium is necessary for health, most people consume much more than their bodies need. This excess sodium, often found in processed foods and restaurant meals, can have serious consequences for heart health, particularly in the form of increased blood pressure.

2 - How Sodium Affects Blood Pressure
When you consume too much sodium, your body retains excess water to balance the sodium levels. This extra fluid in your bloodstream increases the volume of blood circulating through your veins, putting additional pressure on the walls of your arteries. This increased pressure is what we commonly know as high blood pressure or hypertension. Over time, hypertension can damage blood vessels, increase the risk of heart disease, and lead to other complications like stroke and kidney disease.
Daniel M. Sauri, MD
blood pressure 136/56
800 Biesterfield Rd, Elk Grove Village, IL 60007, USA

3 - Health Risks of Excessive Sodium Intake
The dangers of too much salt go beyond just high blood pressure. Chronic high sodium consumption can lead to various health problems, including:
- Heart disease – High sodium levels strain the heart and blood vessels, increasing the risk of heart failure and other cardiovascular conditions.
- Stroke – Long-term high blood pressure, caused by excess sodium, is one of the primary contributors to stroke.
- Kidney damage – The kidneys filter excess sodium from the blood, and too much sodium can damage kidney function, leading to kidney disease.
- Osteoporosis – Excessive sodium can cause the body to excrete calcium, which weakens bones and increases the risk of osteoporosis.
4 - Tips for Reducing Sodium Intake
Reducing your sodium intake can have a significant impact on your heart health and overall well-being. Here are a few strategies to help you cut back on sodium:
- Read food labels – Check for sodium content on food labels, especially in processed foods, canned goods, and frozen meals.
- Cook more at home – Preparing meals at home allows you to control the amount of salt you add to your food.
- Use herbs and spices – Instead of salt, flavor your meals with herbs, spices, garlic, and vinegar.
- Limit fast food and restaurant meals – Restaurant meals and fast food are often high in sodium. Opt for healthier choices or ask for dishes with less salt.
- Drink plenty of water – Staying hydrated helps flush excess sodium out of your body.
5 - How HeartCare Hub Can Help Manage Your Sodium Intake
At HeartCare Hub, we provide resources and products designed to support your heart health. From low-sodium food options to expert advice on maintaining a balanced diet, we are committed to helping you reduce your sodium intake and improve your cardiovascular health. Visit our site for more information and discover products that can help you manage your sodium intake effectively.





















Intermountain Health Primary Children's Hospital
100 mario capecchi dr salt lake city ut 84113
100 Mario Capecchi Dr, Salt Lake City, UT 84113, USA