Understanding High Blood Pressure and Heart Disease
High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is often referred to as the "silent killer" due to its lack of noticeable symptoms. It's a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide and is one of the primary contributors to heart disease. Understanding how high blood pressure leads to heart disease is crucial in preventing severe health issues and taking proactive steps to protect your heart. In this article, we’ll dive deep into the relationship between high blood pressure and heart disease, explore the mechanisms behind it, and discuss how to manage and prevent hypertension to safeguard your cardiovascular health.

1. The Impact of High Blood Pressure on the Heart
When your blood pressure is consistently high, it forces your heart to work harder to pump blood throughout your body. Over time, this extra strain can damage the heart and blood vessels. Specifically, the added pressure can lead to the thickening of the heart muscle (left ventricular hypertrophy), reduced heart efficiency, and weakened arteries. This creates a perfect storm for cardiovascular diseases such as coronary artery disease, heart failure, and even heart attacks.
Atlanta Heart Specialists
atlanta heart specialists
4375 Johns Creek Pkwy #350, Suwanee, GA 30024, USA

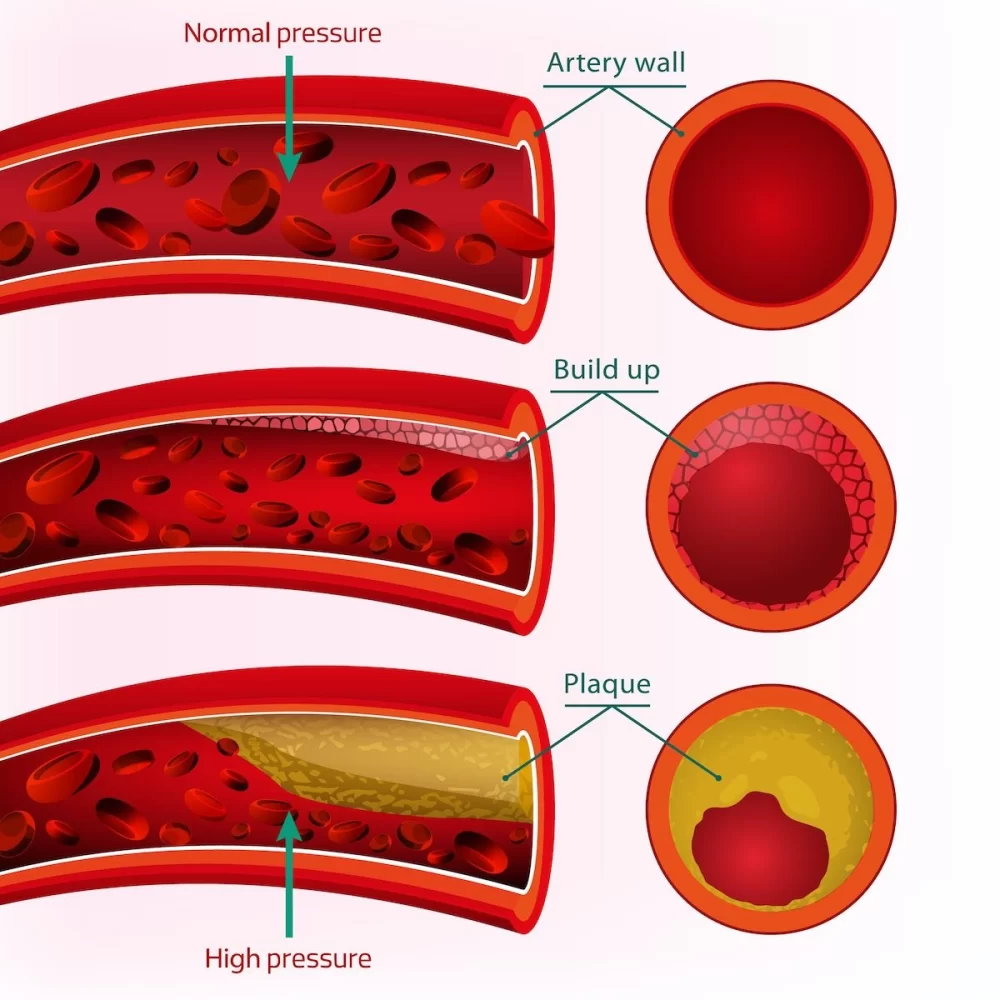
2. How High Blood Pressure Damages the Arteries
High blood pressure causes damage to the lining of the arteries. The blood vessels become narrower and stiffer as a result, making it harder for blood to flow freely. Over time, this narrowing, known as atherosclerosis, can restrict blood flow to vital organs, including the heart. When blood can't flow properly, the heart must work harder to pump blood, which contributes further to the development of heart disease. This can eventually lead to a heart attack if the blood flow to the heart is completely blocked.
3. Hypertension and Increased Risk of Heart Attacks
One of the most serious risks of untreated high blood pressure is its contribution to heart attacks. When blood pressure is too high, it increases the likelihood of plaque buildup in the arteries, leading to a blockage or rupture. This blockage can cut off the blood supply to the heart, resulting in a heart attack. Hypertension not only increases the risk of a heart attack, but it can also worsen the outcomes for those who have already experienced one, as it leads to further strain on the heart and its ability to recover.
4. The Role of Hypertension in Heart Failure
Heart failure is another consequence of untreated high blood pressure. As the heart works harder to pump against elevated blood pressure, the muscle can become enlarged and weakened, eventually causing it to lose its ability to pump blood efficiently. This condition, known as heart failure, occurs when the heart cannot meet the body's demand for oxygenated blood. Hypertension is the leading cause of both left-sided and right-sided heart failure, with the risk increasing with age and the duration of hypertension.
5. How to Manage High Blood Pressure and Prevent Heart Disease
Managing high blood pressure is key to preventing heart disease. The first step is to monitor your blood pressure regularly. If it's consistently high, consult a healthcare provider to discuss lifestyle changes and medications that can help control your blood pressure. Adopting a heart-healthy diet, regular exercise, reducing stress, and limiting alcohol and tobacco use can significantly reduce blood pressure levels. In some cases, medication such as ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, or diuretics may be necessary to control hypertension effectively.
6. The Importance of Regular Check-Ups and Blood Pressure Monitoring
Routine check-ups with your healthcare provider are essential in managing hypertension and preventing heart disease. Monitoring your blood pressure at home and during regular visits to your doctor can provide early warnings of rising blood pressure, allowing for timely interventions. Your doctor may also recommend lifestyle changes, such as a low-sodium diet, regular physical activity, and stress management techniques, all of which can help to lower your blood pressure and protect your heart health.
Conclusion: Protect Your Heart by Managing Blood Pressure
High blood pressure is a major contributor to heart disease, but it can be controlled with the right steps. By understanding how hypertension damages the heart and blood vessels, you can take proactive measures to protect your cardiovascular health. Regular blood pressure monitoring, a healthy lifestyle, and timely medical interventions can help you manage high blood pressure effectively, reducing your risk of heart disease. If you have concerns about your blood pressure, speak with your healthcare provider about the best strategies to lower it and safeguard your heart.





















Deborah Heart and Lung Center
deborah heart and lung center
200 Trenton Rd, Browns Mills, NJ 08015, USA