- 1. Understanding Vitamin B and Heart Health
- 2. The Link Between Vitamin B Deficiency and Heart Disease
- 3. Types of B Vitamins and Their Role in Heart Health
- 4. Symptoms of Vitamin B Deficiency and How It's Diagnosed
- 5. Preventing and Treating Vitamin B Deficiency
1. Understanding Vitamin B and Heart Health
Vitamin B is a group of essential nutrients that play a vital role in various bodily functions, including energy production, brain function, and the maintenance of healthy skin and muscles. What many people don’t realize is that B vitamins are also crucial for cardiovascular health. Deficiencies in these vitamins can contribute to an increased risk of heart disease and other cardiovascular issues.
The B vitamin group consists of eight different vitamins: B1 (thiamine), B2 (riboflavin), B3 (niacin), B5 (pantothenic acid), B6 (pyridoxine), B7 (biotin), B9 (folic acid), and B12 (cobalamin). Each of these vitamins has specific functions that support heart health, and a deficiency in any of them can have a detrimental effect on the heart and blood vessels.

2. The Link Between Vitamin B Deficiency and Heart Disease
Research has shown that a deficiency in certain B vitamins, particularly B6, B9 (folic acid), and B12, is linked to an increased risk of heart disease. The primary reason for this is that these vitamins help regulate homocysteine levels in the blood. Homocysteine is an amino acid that, when elevated, can damage blood vessel walls and increase the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular problems.
Studies have demonstrated that people with low levels of vitamin B6, B9, and B12 tend to have higher levels of homocysteine. This, in turn, can lead to the narrowing of arteries, increased clotting, and inflammation—factors that significantly raise the risk of heart disease. Additionally, deficiencies in these B vitamins can impair the function of the endothelial cells that line the blood vessels, further compromising heart health.
It’s important to note that while vitamin B deficiencies can contribute to heart disease, they are not the sole cause. Other lifestyle factors, such as poor diet, lack of exercise, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption, also play a role in the development of heart disease.
Atlanta Heart Specialists
atlanta heart specialists
4375 Johns Creek Pkwy #350, Suwanee, GA 30024, USA

3. Types of B Vitamins and Their Role in Heart Health
Let’s take a closer look at the specific B vitamins and how they contribute to heart health:
- Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine): Vitamin B6 helps regulate homocysteine levels in the blood, reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease. It also plays a role in the production of red blood cells and the proper functioning of the nervous system, both of which are essential for heart health.
- Vitamin B9 (Folic Acid): Folic acid is one of the most important B vitamins for cardiovascular health. It helps break down homocysteine and convert it into less harmful substances. Folic acid also promotes healthy blood flow and can reduce the risk of high blood pressure and stroke.
- Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin): Like vitamin B6 and B9, vitamin B12 helps regulate homocysteine levels. It also plays a role in the production of red blood cells and the maintenance of healthy nerve cells. Deficiency in vitamin B12 is linked to an increased risk of heart disease and stroke.
4. Symptoms of Vitamin B Deficiency and How It's Diagnosed
Vitamin B deficiencies can be difficult to diagnose because the symptoms can vary widely and are often mistaken for other health issues. However, there are some common signs to look out for:
- Fatigue: One of the earliest signs of a vitamin B deficiency is fatigue, as these vitamins are essential for energy production in the body.
- Anemia: A lack of vitamin B12 or folic acid can lead to megaloblastic anemia, which results in fatigue, weakness, and pale skin.
- Shortness of Breath and Dizziness: Insufficient B vitamins can affect the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood, leading to shortness of breath and dizziness, particularly during physical activity.
- Heart Palpitations: Deficiencies in B vitamins, especially B12, can cause irregular heartbeats or palpitations due to the effect on red blood cell production and oxygen transport.
- Memory Problems and Confusion: A lack of vitamin B12, in particular, can affect brain function, leading to memory problems, difficulty concentrating, and even depression.
If you suspect a vitamin B deficiency, it’s important to see a healthcare provider. A blood test can diagnose deficiencies in B vitamins and help determine the appropriate treatment.
5. Preventing and Treating Vitamin B Deficiency
Preventing vitamin B deficiency is largely about maintaining a balanced diet that includes a variety of foods rich in these essential nutrients. Here are some tips:
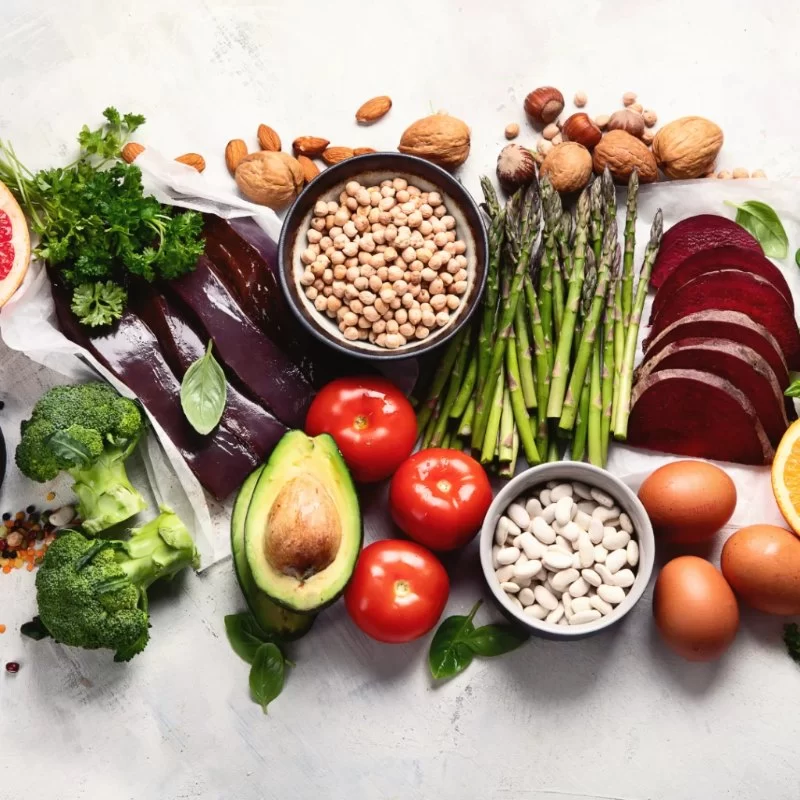
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Foods such as leafy greens, beans, peas, nuts, seeds, fish, poultry, eggs, dairy products, and fortified cereals are all excellent sources of B vitamins. Ensuring a varied and nutrient-rich diet will help prevent deficiencies.
- Consider Supplements: If you have difficulty getting enough B vitamins from your diet, a supplement may be necessary. However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen.
- Monitor Your Health: Regular check-ups and blood tests can help identify any potential deficiencies early. If you’re at risk for heart disease or have a family history of cardiovascular issues, keeping track of your vitamin B levels can be an important preventative measure.
At HeartCare Hub, we offer a variety of heart health supplements, including those rich in B vitamins, to support cardiovascular health. Consult with your healthcare provider to find the right supplements for your needs.




















Deborah Heart and Lung Center
deborah heart and lung center
200 Trenton Rd, Browns Mills, NJ 08015, USA