Pulmonary Embolism: A Serious Complication of DVT
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is one of the most serious and potentially life-threatening complications of deep vein thrombosis (DVT). Understanding how these conditions are related, their risks, and the methods for prevention and treatment is critical for reducing the chances of experiencing such severe complications. This article will provide a comprehensive look at how pulmonary embolism develops from DVT, how to recognize the symptoms, and what steps can be taken to manage and prevent these dangerous conditions.

Understanding DVT and Pulmonary Embolism
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) occurs when a blood clot, typically in the deep veins of the legs, forms and remains stuck in one place. These clots can prevent normal blood flow, leading to swelling, pain, and other complications. If a clot breaks loose, it can travel through the bloodstream, and this is where the danger lies—when it reaches the lungs, it can cause a pulmonary embolism (PE).
Froedtert Menomonee Falls Hospital Cardiac and Pulmonary Rehabilitation
froedtert pulmonary
W180 N, 8085 Town Hall Rd, Menomonee Falls, WI 53051, USA

What Is Pulmonary Embolism?
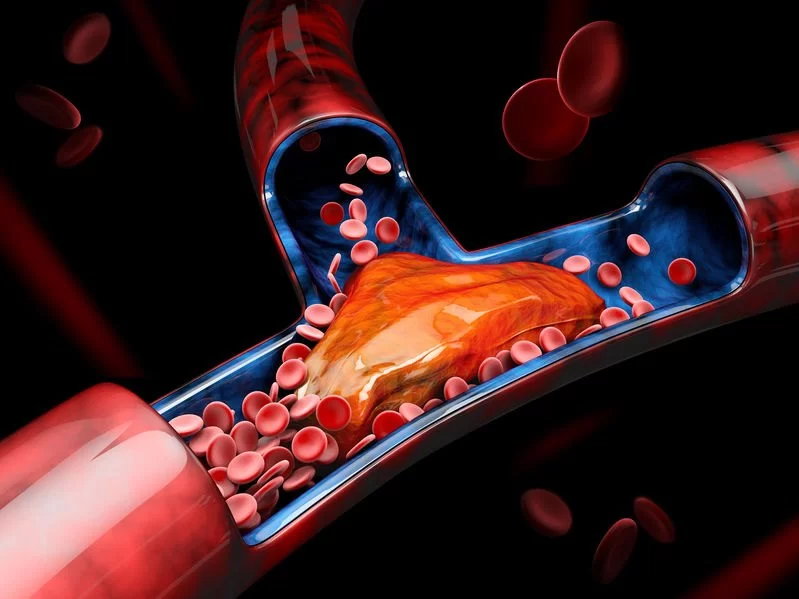
A pulmonary embolism occurs when a blood clot blocks a pulmonary artery, which supplies blood to the lungs. This blockage can reduce the flow of oxygen to the lungs and the rest of the body, potentially leading to severe complications such as heart failure, lung damage, or even death if left untreated.
How DVT Leads to Pulmonary Embolism
When a clot forms in the veins of the legs or pelvis (the most common areas for DVT), it can break off and travel through the veins to the heart, where it is then pumped into the lungs. The clot becomes lodged in one of the pulmonary arteries, causing a blockage that interrupts normal lung function. This is a life-threatening medical emergency that requires immediate attention.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Pulmonary Embolism
Recognizing the symptoms of a pulmonary embolism early is crucial for getting timely treatment. The symptoms can vary depending on the size of the clot and how much of the lung is affected. Common symptoms of PE include:
Common Symptoms of Pulmonary Embolism
- Sudden shortness of breath
- Sharp chest pain that may worsen with deep breathing or coughing
- Coughing up blood
- Rapid or irregular heart rate
- Lightheadedness or fainting
If you or someone you know experiences any of these symptoms, it is important to seek emergency medical care immediately. Pulmonary embolism can be diagnosed through imaging tests like CT pulmonary angiography or ventilation-perfusion scans, and doctors may also use blood tests such as D-dimer to assess the likelihood of a clot.
Prevention and Management of Pulmonary Embolism
Preventing DVT from progressing to a pulmonary embolism is the key to reducing the risk of this dangerous complication. There are several measures that can be taken to manage and reduce the chances of clot formation, as well as steps for dealing with a diagnosed PE.
Preventing DVT and Pulmonary Embolism
To prevent DVT and its associated complications, individuals at risk, such as those with a history of clotting disorders, recent surgeries, or long periods of immobility, should take proactive measures:
- Stay active and avoid prolonged periods of immobility, especially on long flights or car rides.
- Wear compression stockings to improve blood circulation.
- Take prescribed blood-thinning medications, as directed by a healthcare provider, to prevent clot formation.
- Maintain a healthy weight and diet, as obesity is a significant risk factor for both DVT and PE.
- Engage in regular physical activity to promote healthy circulation.
Managing Pulmonary Embolism
If a pulmonary embolism is suspected or diagnosed, immediate medical treatment is essential. Treatment options include:
- Anticoagulants (blood thinners) to prevent further clot formation.
- Thrombolytics (clot-busting drugs) in severe cases to dissolve large clots quickly.
- In some cases, surgery or a catheter-directed procedure may be necessary to remove the clot.
Early detection and rapid treatment are crucial to reducing the risks of severe complications or death associated with PE. A healthcare provider will determine the best course of treatment based on the individual’s health condition and the severity of the embolism.
The Role of HeartCare Hub in Managing Cardiovascular Health
At HeartCare Hub, we provide vital resources and expert advice on managing cardiovascular health, including understanding conditions like DVT and pulmonary embolism. Our platform offers access to top-quality services, tools, and information to help you manage your heart health and prevent complications like PE.
Stay informed about the latest developments in cardiovascular diagnostics, and take proactive steps to ensure your heart health. Visit our website to explore the best products, services, and resources for your specific needs.





















Capital Health Medical Center – Hopewell
capital health pulmonary
1 Capital Way, Pennington, NJ 08534, USA