How High Cholesterol Leads to Heart Disease
High cholesterol is one of the most common health conditions that affects millions of people worldwide, particularly in the United States. Many individuals might not realize that cholesterol levels have a profound impact on heart health. While cholesterol is necessary for the body to build cells and produce hormones, too much of it in the bloodstream can lead to serious cardiovascular problems, including heart disease.

The Basics of Cholesterol and Heart Disease
Cholesterol is a waxy substance found in every cell of your body. It is carried through the bloodstream by two types of lipoproteins: Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL), often referred to as “bad cholesterol,” and High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL), known as “good cholesterol.”
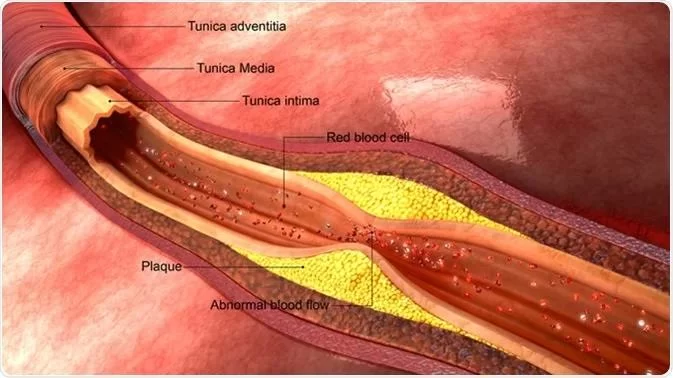
When your LDL cholesterol levels are too high, it can begin to build up in the walls of your arteries, leading to a condition called atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis causes the arteries to narrow and stiffen, which impedes blood flow and puts extra strain on the heart. This can ultimately lead to heart disease, heart attacks, and strokes.
Atlanta Heart Specialists
atlanta heart specialists
4375 Johns Creek Pkwy #350, Suwanee, GA 30024, USA

The Process of Cholesterol Buildup
Over time, high cholesterol can contribute to the formation of plaques in the arteries. These plaques consist of fatty deposits, cholesterol, and other substances that accumulate in the artery walls. As the plaques grow, they reduce the available space for blood to flow, which can lead to a host of cardiovascular issues.
Imagine trying to push a large object through a narrow, constricted space. Similarly, when your arteries are clogged with plaque, your heart struggles to pump oxygen-rich blood to the organs and tissues that need it most. This restricted blood flow can cause severe damage to the heart and increase the risk of heart attacks or heart failure.
Risk Factors for High Cholesterol and Heart Disease
There are several factors that increase your risk of developing high cholesterol and heart disease:
- Diet: Eating foods high in saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol can raise your LDL cholesterol levels.
- Lack of Exercise: Physical inactivity can lead to weight gain and higher cholesterol levels, which negatively impact heart health.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese increases your chances of developing high cholesterol, which in turn raises the risk of heart disease.
- Genetics: Some people inherit genes that cause high cholesterol, putting them at a higher risk of cardiovascular issues.
- Smoking: Smoking damages the blood vessels, increases LDL cholesterol, and decreases HDL cholesterol, all of which contribute to heart disease.
- Age and Gender: As people age, cholesterol levels tend to rise. Additionally, men are more likely to develop heart disease at an earlier age than women.
How Cholesterol Affects Your Heart Health
The relationship between cholesterol and heart disease is not just about the levels of LDL and HDL cholesterol. The size and type of cholesterol particles also play a critical role. Smaller, denser LDL particles are more likely to penetrate the walls of arteries, leading to plaque buildup. Larger, fluffier particles, on the other hand, are less likely to cause damage.
Moreover, high cholesterol levels can lead to the thickening of the heart's walls, which in turn makes it more difficult for the heart to pump blood effectively. This increased workload can lead to heart failure over time, making it harder for your body to get the oxygen it needs to function properly.
How to Prevent Heart Disease by Managing Cholesterol Levels
There are various steps you can take to lower your cholesterol and reduce the risk of heart disease. Here are some practical tips that can help you manage your cholesterol levels:
1. Adopt a Heart-Healthy Diet
Focus on eating foods that are high in fiber, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes. These foods help lower LDL cholesterol levels. Additionally, include healthy fats in your diet, such as those found in olive oil, nuts, and fatty fish like salmon and mackerel. Avoid processed foods, red meats, and foods high in trans fats, as they can contribute to higher cholesterol levels.
2. Get Regular Exercise
Exercise can help raise HDL cholesterol levels while lowering LDL cholesterol. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise on most days of the week. Activities like walking, cycling, and swimming can improve heart health and support healthy cholesterol levels.
3. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Carrying excess weight, especially around your midsection, increases the risk of high cholesterol and heart disease. Losing weight through a combination of healthy eating and regular physical activity can help lower your cholesterol and improve heart health.
4. Quit Smoking and Limit Alcohol Intake
Smoking damages the blood vessels, increases LDL cholesterol, and lowers HDL cholesterol. Quitting smoking is one of the most important steps you can take to protect your heart. Additionally, drinking alcohol in moderation (or not at all) can help maintain healthy cholesterol levels.
5. Consider Medication If Necessary
For individuals with very high cholesterol levels or those who are at high risk for heart disease, doctors may recommend cholesterol-lowering medications like statins. These medications can help reduce LDL cholesterol and improve heart health when lifestyle changes alone are not enough.
Real-Life Example: A Story of Heart Disease Prevention
Meet John, a 52-year-old man who had been living a sedentary lifestyle and consuming a diet rich in fast food. John’s cholesterol levels were alarmingly high, and he was diagnosed with early-stage heart disease. However, with the guidance of his healthcare team, John made significant changes to his lifestyle. He started exercising regularly, switched to a plant-based diet, and reduced his stress levels. Within a year, his cholesterol levels dropped dramatically, and he no longer had symptoms of heart disease. John's story highlights the power of prevention and lifestyle changes in protecting heart health.
Heart disease is a serious condition, but with proactive management of cholesterol levels, you can significantly reduce your risk. Make heart-healthy choices today to ensure a long, healthy life.





















Deborah Heart and Lung Center
deborah heart and lung center
200 Trenton Rd, Browns Mills, NJ 08015, USA