Understanding the Impact of Family History on Heart Disease
Heart disease is a leading cause of death in the United States, and many of us are concerned about our heart health. While lifestyle factors such as diet, exercise, and smoking play a significant role in heart disease, one factor that is often overlooked is family history. If you have close relatives who have experienced heart disease, your risk may be higher. In this article, we’ll explore how family history impacts your risk of heart disease and what you can do to protect your heart.

What Is the Role of Family History in Heart Disease?
When we talk about family history and heart disease, we’re referring to the presence of cardiovascular problems among your immediate family members, such as parents, siblings, or grandparents. This genetic component plays an essential role in the likelihood of developing heart disease. If your parents or siblings had heart disease, it could indicate an inherited risk that might increase your chances of developing similar health issues.
But it’s not just about genetics. The lifestyle choices made by your family members, such as diet and exercise habits, can also contribute to the overall risk. Understanding your family's medical history can help you make informed decisions and take preventative measures to reduce your risk.
Atlanta Heart Specialists
atlanta heart specialists
4375 Johns Creek Pkwy #350, Suwanee, GA 30024, USA

The Science Behind Genetic Factors and Heart Disease
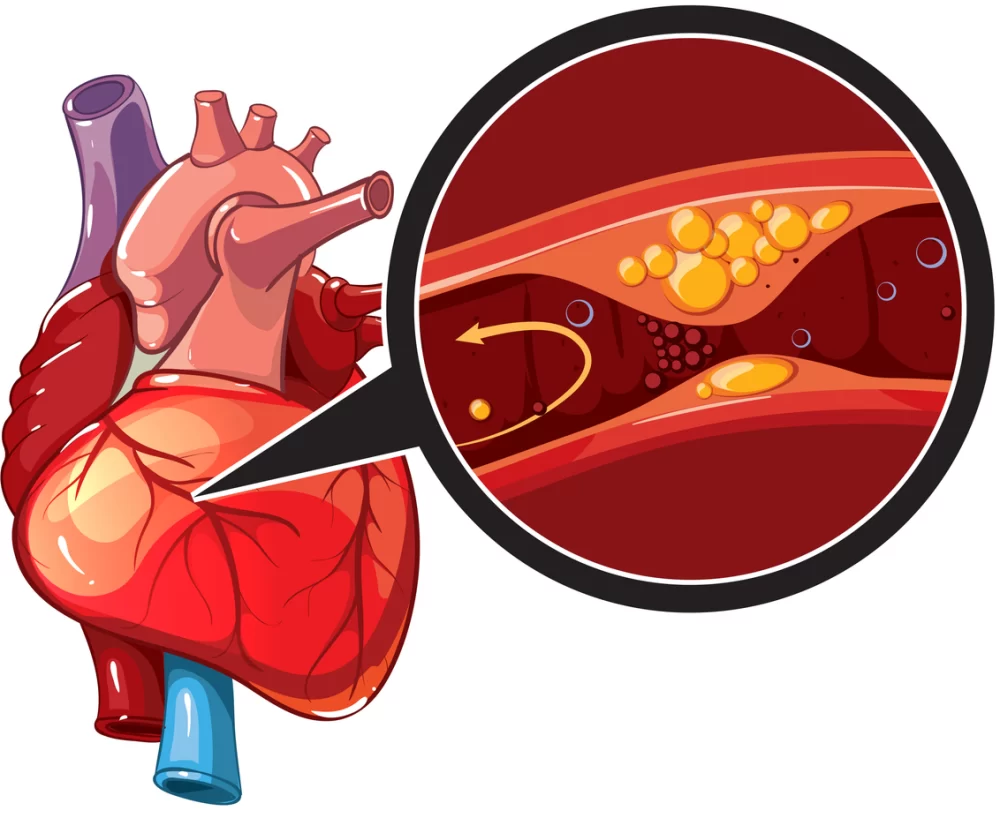
Genetic factors influence how your body processes cholesterol, blood pressure, and other key cardiovascular functions. These factors can increase your likelihood of developing conditions such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and atherosclerosis, all of which are significant contributors to heart disease. For example, some people inherit genes that cause higher levels of LDL cholesterol (the "bad" cholesterol), which can lead to plaque buildup in arteries, raising the risk of heart attack or stroke.
Studies have shown that heart disease tends to run in families, indicating a genetic component. For instance, having a parent who suffered from heart disease before the age of 55 can significantly raise your risk. Researchers have identified multiple genes linked to heart disease, but much is still to be understood about how genetics contribute to heart health.
How to Assess Your Risk Based on Family History
It’s important to have an open conversation with your doctor about your family’s medical history. You may want to prepare by gathering details about your family members' health conditions, particularly any instances of heart disease, diabetes, or high cholesterol. This information will help your healthcare provider assess your risk more accurately and suggest the appropriate steps for prevention.
Risk factors are typically categorized into two groups: modifiable and non-modifiable. Family history falls into the non-modifiable category because it’s something you can’t change. However, understanding your genetic predisposition can help you address modifiable risk factors—like maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, and exercising regularly—to reduce your overall risk.
Preventive Measures You Can Take to Protect Your Heart
Even if you have a family history of heart disease, there are plenty of things you can do to prevent cardiovascular issues from developing. Here are some important steps you can take:
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: Eating a heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats can help lower your cholesterol and blood pressure, reducing your risk of heart disease.
- Exercise Regularly: Physical activity is one of the best ways to improve heart health. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week to strengthen your heart and improve circulation.
- Monitor Your Cholesterol and Blood Pressure: Regular checkups with your doctor can help you track important heart health metrics like cholesterol levels and blood pressure. Early detection allows for prompt treatment and better outcomes.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress is linked to various heart problems, including high blood pressure and heart attacks. Finding ways to manage stress through relaxation techniques, meditation, or mindfulness can benefit your heart.
The Importance of Regular Screenings and Checkups
Even if you don’t have noticeable symptoms, it’s essential to stay proactive about your heart health. Regular screenings for blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar can help catch potential issues early. For those with a family history of heart disease, starting these screenings earlier in life can be particularly important. By working closely with your healthcare provider, you can tailor a prevention plan specific to your needs.
Conclusion: The Key to Heart Disease Prevention
In conclusion, family history plays a crucial role in your heart disease risk. While you can’t change your genetic makeup, you can control many aspects of your lifestyle that contribute to cardiovascular health. By understanding the connection between genetics and heart disease, staying on top of regular screenings, and following heart-healthy habits, you can protect yourself and reduce your chances of developing serious cardiovascular conditions. Remember, prevention is always better than treatment, and being proactive about your heart health is the best way to ensure a long, healthy life.





















Deborah Heart and Lung Center
deborah heart and lung center
200 Trenton Rd, Browns Mills, NJ 08015, USA