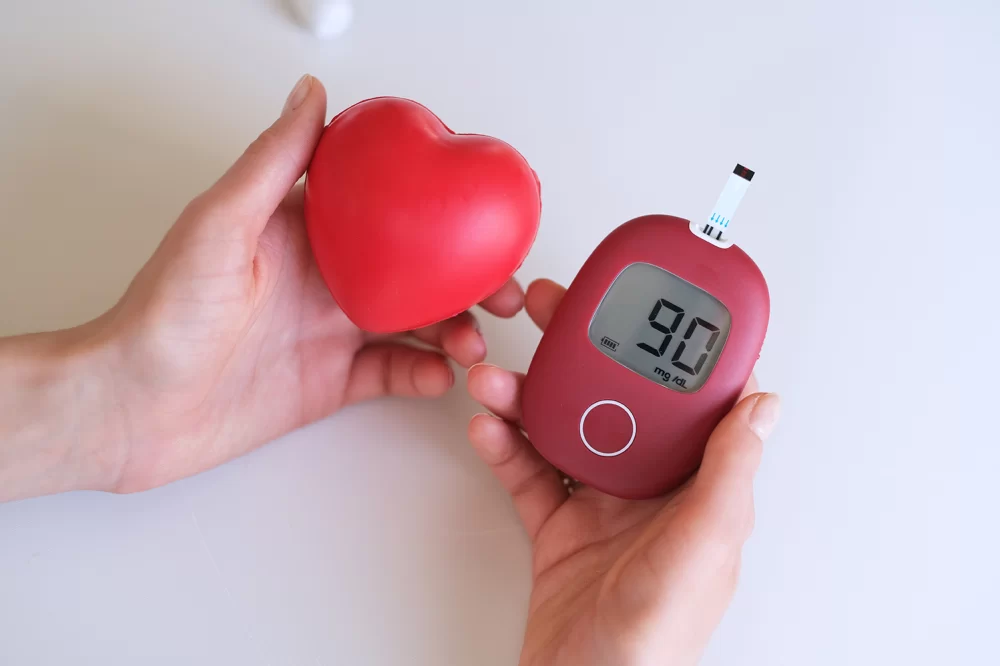
The Link Between Diabetes and Heart Disease
Diabetes, particularly when left unmanaged, can significantly affect your heart health. While diabetes itself is a condition that affects your body’s ability to regulate blood sugar, its effects extend well beyond just blood glucose levels. One of the most significant and often overlooked consequences of diabetes is its impact on heart health. Understanding this connection is vital in managing both conditions effectively.

How High Blood Sugar Affects Your Heart
When blood sugar levels are too high over a prolonged period, it can damage blood vessels and the nerves that control the heart. High blood sugar leads to a process known as "glycation," where sugar molecules bond with proteins in the body, causing them to become stiff and less functional. This damage to the blood vessels increases the risk of developing atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries), which can lead to heart disease. Over time, this stiffening of blood vessels can make it more difficult for the heart to pump blood effectively, raising the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
Capital Health Medical Center – Hopewell
capital health medical center hopewell
1 Capital Way, Pennington, NJ 08534, USA

Diabetes and Cardiovascular Risk: The Compounding Effects
People with diabetes often suffer from other conditions that further increase their risk of heart disease. High blood pressure (hypertension), high cholesterol levels, and obesity are common among individuals with diabetes. Each of these conditions can damage the cardiovascular system, and when combined with diabetes, they create a compounded risk factor for developing severe heart problems.
For example, high blood pressure causes added strain on the heart and blood vessels, while high cholesterol levels lead to plaque buildup in arteries, making it harder for blood to flow. Together with diabetes, these conditions can increase the risk of having a heart attack, heart failure, or stroke. It's a dangerous combination that calls for careful monitoring and management.
Real-Life Stories: How Diabetes Affects Heart Health
Take the story of Mark, a 55-year-old man who was diagnosed with type 2 diabetes five years ago. Initially, Mark didn't worry much about his condition, thinking it only affected his blood sugar levels. However, over time, he began noticing symptoms of chest pain and shortness of breath. After visiting his doctor, he learned that his uncontrolled diabetes had contributed to developing cardiovascular disease, including coronary artery disease. Mark's story is not unique. Thousands of people with diabetes unknowingly risk their heart health until it’s too late.
Another example is Sarah, a 45-year-old woman with a family history of heart disease. She had been living with type 1 diabetes for nearly 20 years. Despite her best efforts to manage her blood sugar, Sarah developed high cholesterol and hypertension, two common conditions that accompany diabetes. She faced several complications with her heart, including angina, which was directly linked to her diabetes. Her doctors emphasized that managing both her blood sugar and cardiovascular health was essential to avoid severe heart-related events.
Preventive Measures to Protect Your Heart
The good news is that you can take proactive steps to manage both diabetes and your heart health. Here are some preventive measures that can significantly reduce the risk of heart disease:
1. Keep Your Blood Sugar Levels in Check
The most important step you can take is to manage your blood sugar levels. This involves a combination of diet, exercise, and medication. Regularly monitoring your blood glucose and following a healthy eating plan designed for diabetes management can help reduce your risk of heart disease.
2. Control Your Blood Pressure
High blood pressure is common in people with diabetes and can cause further strain on your heart. Regular check-ups and medication, when necessary, can help keep your blood pressure within healthy limits.
3. Eat a Heart-Healthy Diet
A balanced, heart-healthy diet is crucial. Focus on whole grains, lean proteins, and plenty of fruits and vegetables. Avoid trans fats, excess sugar, and salt, all of which can exacerbate both diabetes and heart disease.
4. Stay Active
Exercise is beneficial for managing both diabetes and heart health. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate physical activity most days of the week. Exercise helps lower blood sugar levels, improves blood circulation, and strengthens the heart.
5. Take Medications as Prescribed
If your doctor has prescribed medication to manage your diabetes or blood pressure, it’s crucial to take it as directed. Skipping doses or discontinuing treatment can worsen both your blood sugar levels and heart health.
6. Regular Health Check-Ups
Frequent check-ups with your healthcare provider are essential to monitor your overall health. Regularly test your blood sugar, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels to stay ahead of potential issues and take corrective action as needed.
The Importance of Early Diagnosis
Early diagnosis of both diabetes and any associated heart conditions can save lives. By detecting issues early on, you can work with your healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses both conditions simultaneously, helping you live a healthier life.
Ultimately, understanding the connection between diabetes and heart disease is key to protecting your health. While the risks are significant, with the right strategies in place, you can reduce the impact of diabetes on your heart and live a long, fulfilling life. Remember that diabetes management is not just about controlling blood sugar—it’s about maintaining overall health and preventing complications that could affect your heart, your quality of life, and your future.





















Deborah Heart and Lung Center
deborah heart and lung center
200 Trenton Rd, Browns Mills, NJ 08015, USA